Technical Post | A Brief Discussion on the Transdermal Absorption of Cosmetics
Percutaneous Absorption
Percutaneous absorption of cosmetics refers to the process by which functional ingredients in cosmetics act on the skin surface or penetrate the epidermis or dermis, accumulating and exerting their effects at that site, according to the product's effectiveness.
Cosmetics are products that act on the surface of the human body, and the skin on the surface of the human body has physical and biochemical barrier functions for the absorption and transmission of exogenous substances. Percutaneous absorption research is an indispensable part of the efficacy and safety evaluation of cosmetics.
I. What is percutaneous absorption:
When using skin care products, there is often a description of "XX product has good skin feel and good absorption", but the "absorption" mentioned in this description is a change in texture/skin feel caused by the evaporation of water/volatile silicone oil, etc., in the product, which can be considered "false absorption".
What is discussed here is "true absorption", which refers to the process by which cosmetic ingredients act on the skin surface or penetrate different skin layers such as the epidermis or dermis, accumulating and exerting their effects at that site. Percutaneous absorption is a double-edged sword; on the one hand, we hope that effective ingredients can penetrate the skin barrier to exert their effects, while on the other hand, excessive percutaneous absorption can also lead to irritation and safety risks.
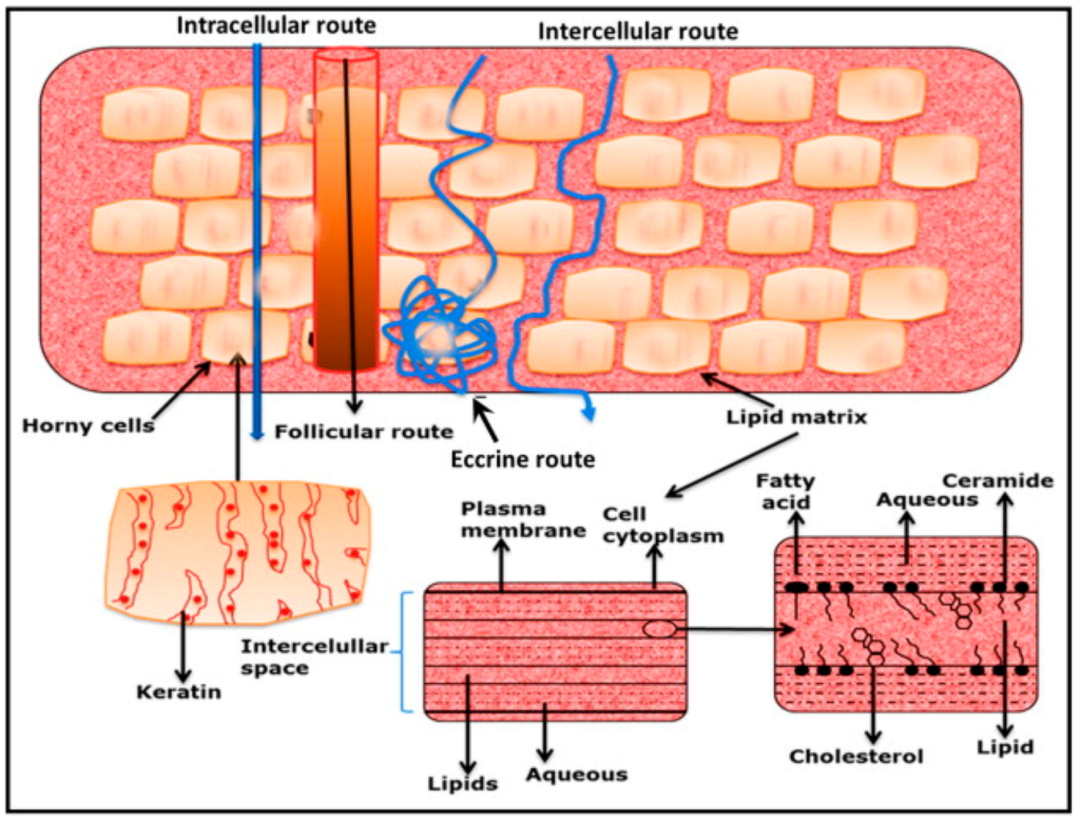
Percutaneous Absorption Routes
The main routes of percutaneous absorption of cosmetics include: Stratum corneum, hair follicles and sebaceous glands, and sweat ducts , the latter two are often referred to as "bypass routes", while Stratum corneum route can be divided into ① Intercellular route and ② Transcellular route 。
1、 Intercellular route: The active substance bypasses the corneocytes and penetrates under the skin through the intercellular substance continuously distributed between the corneocytes;
2、 Transcellular route: The active substance directly passes through the corneocytes and intercellular substance, alternately diffusing in the aqueous and lipid phases.
It is generally believed that lipid-soluble, non-polar substances easily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the intercellular space; while water-soluble, polar substances easily diffuse through the corneocytes.
Among them, although the intercellular space only accounts for about 30% of the total volume of the stratum corneum, it plays a major role in transdermal penetration because its lipid resistance is smaller than that of corneocytes.
II. The Role of Percutaneous Absorption in Efficacy Evaluation
When conducting cosmetic efficacy research, percutaneous absorption generally evaluates the amount of effective ingredients entering the skin and does not need to evaluate the amount of effective ingredients passing through the skin into the systemic circulation.
The absorption of effective ingredients is closely related to the formulation system, product pH value, etc. Taking vitamin C as an example, the percutaneous absorption of VC is related to the pH value and the amount of formulation added: VC absorption is most significant at pH=2, and its percutaneous absorption rate increases with increasing concentration below 20%, and decreases with increasing concentration above 20%. [1] 。
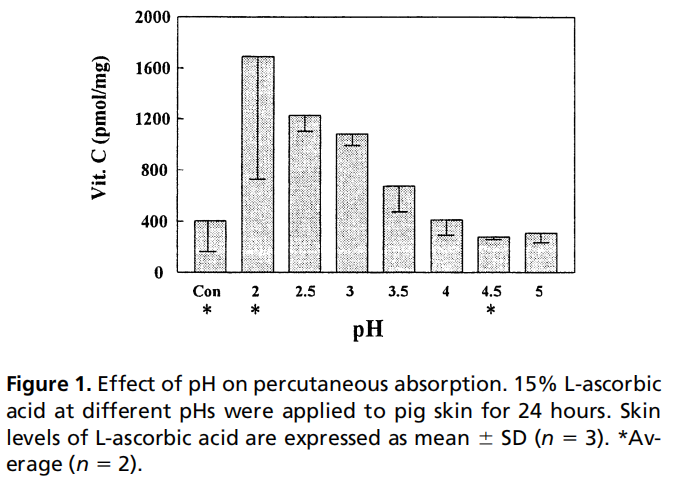
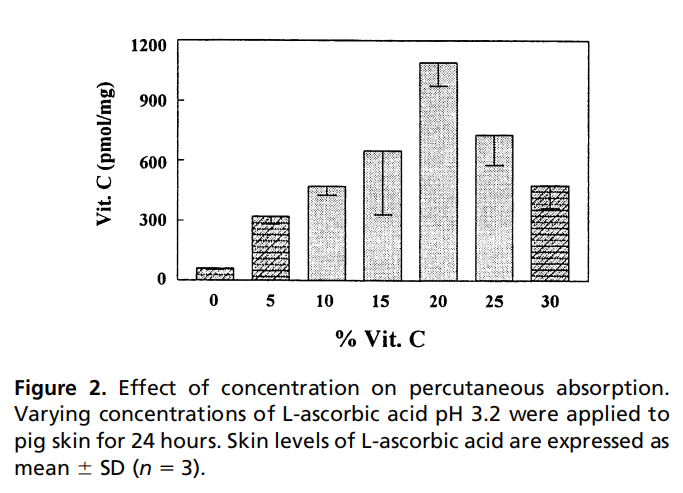
Percutaneous absorption in efficacy research can guide formulators to develop formulations in a targeted manner, allowing effective ingredients to exert their effects more fully.
The Role of Percutaneous Absorption in Safety Evaluation
When conducting cosmetic safety evaluation, it is necessary to evaluate the amount of ingredients entering the systemic circulation, and the study of percutaneous absorption is even more important. The "Technical Guidelines for Cosmetic Safety Assessment (2021 Edition)" 5.11 clearly requires:
1. In the absence of percutaneous absorption data, the absorption rate is calculated as 100%; if the absorption rate is not 100%, relevant explanations must be provided;
2. Molecular weight >500 Daltons, highly ionized, Log Pow≤-1 or ≥4, topological polar surface area >120Å 2 , melting point >200℃, absorption rate is calculated as 10% ;
3. If a polymer is composed of one or more structural units linked by covalent bonds, with an average relative molecular mass >1000 Daltons and the content of oligomers with a relative molecular mass <1000 Daltons <10%, and the structure and properties are stable, percutaneous absorption can be disregarded.
Taking the commonly used anti-hair loss agent pyridoxyl diaminopyrimidine oxide (Minoxidil) as an example, we confirmed in our experiments that this ingredient is difficult to penetrate the skin barrier and enter the systemic circulation, and the amount entering the systemic circulation is below 4% of the added amount under different experimental conditions, which is comparable to its homolog Minoxidil. [3] 。
Without conducting percutaneous absorption research, according to the requirements of the "Technical Guidelines for Cosmetic Safety Assessment (2021 Edition)", the margin of safety (MoS) needs to be calculated at an absorption rate of 100%, resulting in a 25-fold difference and a significant impact on the safety assessment conclusion.
III. Percutaneous Absorption Test Methods:
Percutaneous absorption tests are divided into in vivo and in vitro tests.
① In vivo test Generally refers to calculating the percutaneous absorption amount by measuring the amount of target substance excreted from the body through urine and excreta. In practice, in vivo experiments are subject to many factors, such as detection methods, ethical constraints, and unclear metabolites. For cosmetics, in vivo experiments are generally not used.
Unless absolutely necessary, such as establishing a comparison between in vivo and in vitro methods, confirming the skin absorption of special active substances, etc., GB/T 27825-2011 "Chemicals Skin Absorption In Vivo Test Method" can be referred to, using hairless nude mice for in vivo research.
② In vitro test Is the mainstream method for cosmetic percutaneous absorption tests, mainly including In vitro diffusion cell method, artificial permeability membrane and mathematical model Among them, the diffusion cell test is the best method for evaluating the percutaneous permeability of compounds.
In short, the diffusion cell method involves mounting excised human or animal skin on a diffusion cell, collecting the receiving solution at regular intervals, determining the content of the active ingredient using a suitable analytical method, and calculating the permeation rate to evaluate the permeation characteristics of the chemical. Diffusion cells can be divided into Static diffusion cell and Dynamic diffusion cell Two major categories

Diffusion cell method and its characteristics
Static diffusion cells include two types: Franz diffusion cells and Valia-Chien diffusion cells. Among them, the Franz diffusion cell is a vertical diffusion cell, which is currently the most commonly used and is widely used in percutaneous absorption experiments for drugs and cosmetics.
In vitro tests can refer to GB/T 27818-2011 "Chemical Products - Skin Absorption - In Vitro Test Method".
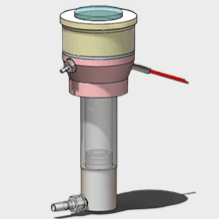
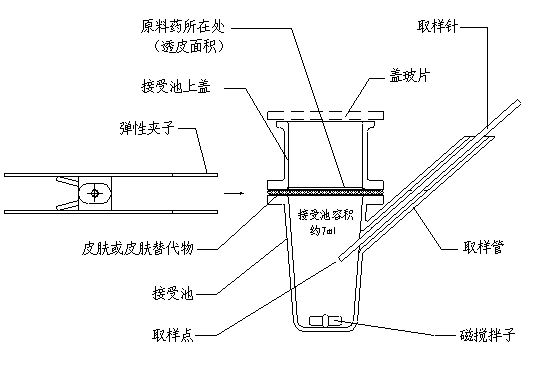
Schematic diagram of Franz diffusion cell
IV. BoRui Pharmaceutical's Percutaneous Absorption Research Platform
BoRui Pharmaceutical's percutaneous absorption research platform consists of the American Logan SYSTEM 918-6 dry-heated automatic percutaneous system, as well as detection and analysis equipment such as high-performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, and mass spectrometry.
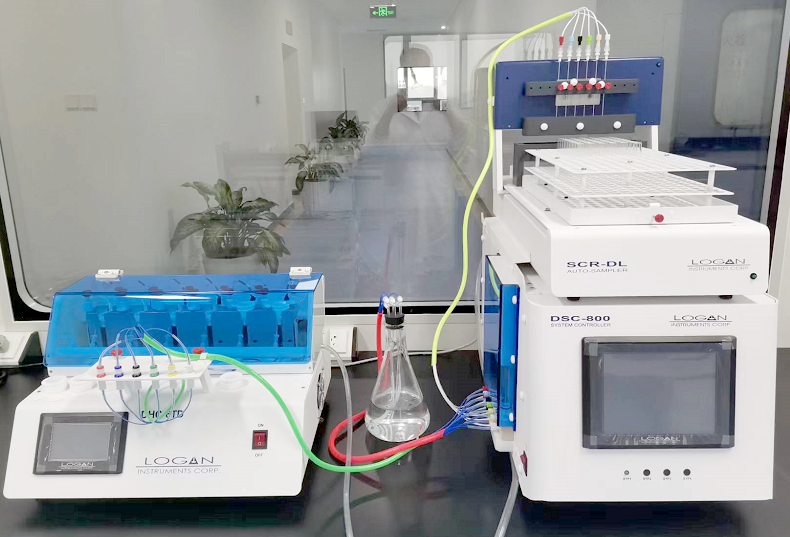

Percutaneous absorption instrument
American Logan is a leading manufacturer in the field of percutaneous absorption. SYSTEM 918-6 is a fully automatic 6-position percutaneous diffusion system with a new technology and modular design. It consists of multiple modules, including 2 DHC-6TD dry-heated percutaneous diffusion instruments, a SCR-DL sample collector, a SYP-12L-10mL injection pump, and a DSC-800 system controller. It has advantages such as an automatic bubble removal function to effectively avoid the influence of bubbles on the experiment; an automatic sampling system for high experimental efficiency; a high-precision injection pump for accurate and rapid sampling; and a dry heating method for high heating efficiency and stable temperature.
V. Application Cases
Percutaneous absorption test of 4-n-butylresorcinol
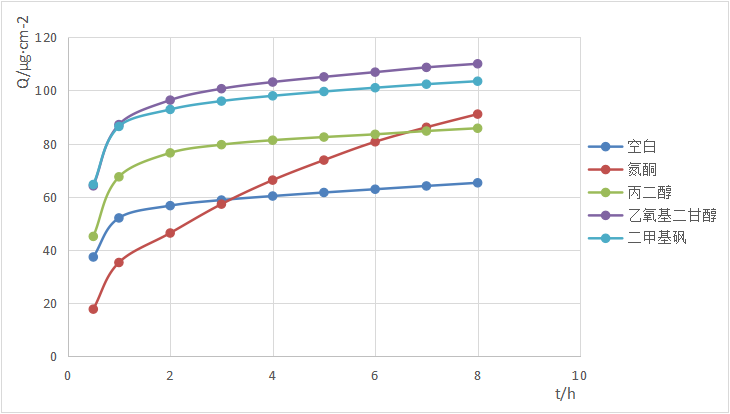
4-n-butylresorcinol is a commonly used whitening agent that can effectively inhibit tyrosinase activity, inhibit melanin production, and improve skin dullness and blemishes. [7] However, it has certain irritation. When the dosage is too high, it is easy to produce a stinging sensation, and in severe cases, it may even cause contact dermatitis and other skin problems. [8] Therefore, how to safely and effectively apply 4-n-butylresorcinol is of great significance.
We measured the cumulative percutaneous penetration of 4-n-butylresorcinol with different penetration enhancers in the essence liquid system. The results are shown in the figure above.
In this system, laurocapram (azone) reduces the percutaneous penetration of 4-n-butylresorcinol in the first 30 minutes, which can effectively reduce the stinging sensation; in the subsequent 2-8 hours, the absorption rate does not significantly decrease, allowing 4-n-butylresorcinol to continuously penetrate and absorb, making it a suitable formulation for 4-n-butylresorcinol.
Summary:
1、 Whether a cosmetic product can be effective depends on whether the skin can absorb the corresponding active ingredients.
2、 Only talking about the efficacy of ingredients without talking about percutaneous absorption will instead become a burden on the skin, increasing the degree of skin damage.
3. Good cosmetics are not a simple accumulation of raw materials. The compatibility of raw materials, the synergistic effect of raw materials, and other technologies are all to ensure that cosmetics better serve consumers.
In order for the active ingredients of cosmetics to be better absorbed, BoRui Pharmaceutical's R&D engineers are constantly trying and making progress in enhancing the absorption of active ingredients, striving to find breakthroughs and create "new power" for products.
References:
1. Pinnell SR, Yang H, Omar M, Monteiro-Riviere N, DeBuys HV, Walker LC, Wang Y, Levine M. Topical L-ascorbic acid: percutaneous absorption studies. Dermatol Surg. 2001 Feb;27(2):137-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00264.x. PMID: 11207686.
2. "Technical Guidelines for Cosmetic Safety Assessment (2021 Edition)"
3. Novak E, Franz TJ, Headington JT, Wester RC. Topically applied minoxidil in baldness. Int J Dermatol. 1985 Mar;24(2):82-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1985.tb05381.x. PMID: 3886571.
4. GB/T 27825-2011 "Chemical Products - Skin Absorption - In Vivo Test Method"
5. GB/T 27818-2011 "Chemical Products - Skin Absorption - In Vitro Test Method"
6. OECD 428: OECD GUIDELINE FOR THE TESTING OF CHEMICALS-Skin Absorption: In Vitro Method
7. Kim DS, Kim SY, Park SH, Choi YG, Kwon SB, Kim MK, Na JI, Youn SW, Park KC. Inhibitory effects of 4-n-butylresorcinol on tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Dec;28(12):2216-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.2216. PMID: 16327152.
8. Lapeere H, De Keyser E. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by 4-n-butylresorcinol present in a night cream for skin hyperpigmentation. Contact Dermatitis. 2020 Aug;83(2):134-135. doi: 10.1111/cod.13543. Epub 2020 Apr 22. PMID: 32243593.
9. Zheng Junmin. New dosage forms for transdermal drug delivery [M]. People's Health Press, 2006.

Welcome to follow our company's WeChat official account to learn more about the latest product information!
More Explore






